obesity and many more life-threatening risk factors, one of the most leading cause of death and a dominant barrier to increase life expectancy in modern world is cancer. According to GLOBOCAN 2020, an estimated of 19.3 million new cancer cases (18.1 million excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) and nearly 10.0 million cancer deaths (9.9 million excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) has occurred, led cancer to ranks first or second main cause of death in nearly 112 or 183 countries and third or fourth in further 23 countries. On the basis of an estimation 1 in 3 people in the US are affected by cancer. According to the latest ranks and epidemiologic trends, cancer’s rising prominence as a leading cause of death, which leads to cardiovascular disease ranks suppressed by cancer as a dominant cause of death. According to the latest cancer estimation, Breast cancer is the most leading type of cancer, with 284,200 new cases expected in the US in 2021, the next most common cancers are lung cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, non-melanoma skin cancer and stomach. The most common causes of cancer death in 2020 were lung, colorectal, liver, stomach and breast cancer.
Targeted therapies are now new class of interest for cancer due to the advantages efficacy, selectivity and safety by acting on specific targets involved in proliferation and differentiation of cancer cells with minimal activity on normal cells compared with traditional oncologic ones. Small molecule inhibitors are one of the targeted cancer therapies, you can easily spot small molecule medicines because their generic name ends in “-ib.” By December 2020, 89 small-molecule targeted antitumor medicines have been approved by the US FDA.
Hence, one of Parsian’s biggest fields of activity is research and development in oncology to manufacture active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and Granules of small-molecule targeted antitumor medicines along with other cancer treatments with the highest global standards to help patients battling with cancer to be cured in a better way by the latest guidelines and with the lowest adverse effects.
Oncology
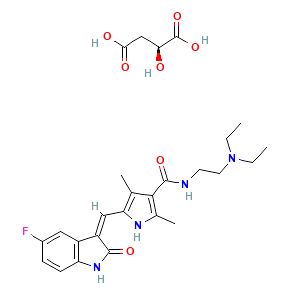
Cas No: 341031-54-7
Mechanism Of Action: Sunitinib is a small molecule that inhibits multiplereceptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), some of which are implicated in tumor growth, pathologic angiogenesis, and
Oncology
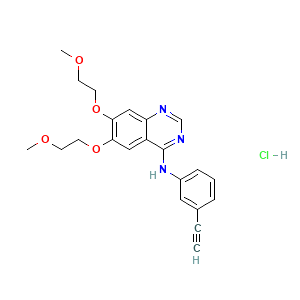
Cas No: 183319-69-9
Mechanism Of Action: Erlotinib is belonged to the group ‘EGFR inhibitors’. It can block EGFRs, which is found on some tumor cells, as a result
Oncology
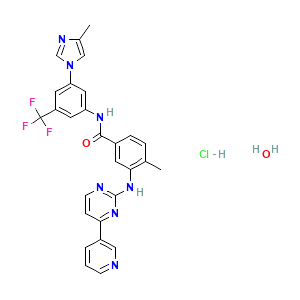
Cas No: 923288-90-8
Mechanism Of Action: Nilotinib can inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of the BCR-ABL protein; CML is caused by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Nilotinib can overcome resistance
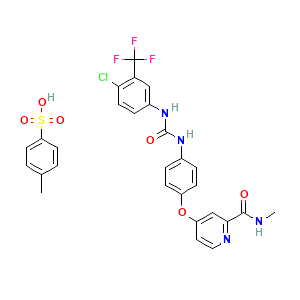
oncology
Cas No: 475207-59-1
Mechanism Of Action: Sorafenib has demonstrated decreased tumor cell proliferation in vitro. It was shown to inhibit multiple intracellular (c-CRAF, BRAF, and mutant BRAF) and
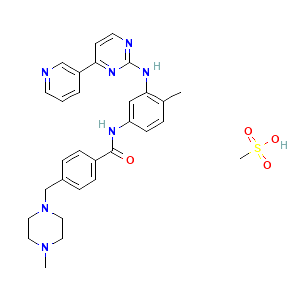
oncology
Cas No: 220127-57-1
Mechanism Of Action: Imatinib mesylate is a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits the bcr-abl tyrosine kinase, the constitutive abnormal tyrosine kinase created by the Philadelphia
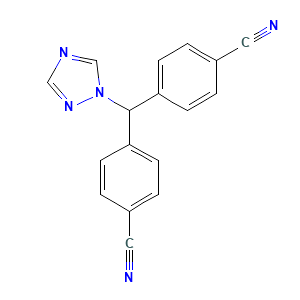
ONCOLOGY
Cas No: 112809-51-5
Mechanism Of Action Letrozole: Letrozole works by blocking the enzyme aromatase, which turns the hormone androgen into small amounts of estrogen in the body, leads