Mechanism Of Action:
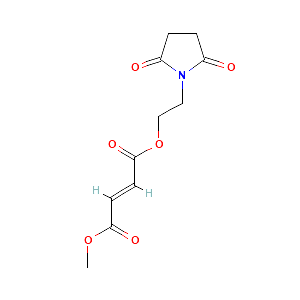
Diroximel fumarate is believed to modulate cell signaling pathways, leading to favorable immune and neuroprotective effects. Monomethyl fumarate (MMF) serves as the active metabolite of diroximel fumarate and triggers the activation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway in humans. This pathway is known to respond to oxidative stress within cells.
Indication:
Multiple Sclerosis
This medication is used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), which include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease.
Diroximel fumarate undergoes metabolism to produce the pharmacologically active metabolite, monomethyl fumarate (MMF), which is also found in dimethyl fumarate. Therefore, the effectiveness of diroximel fumarate is based on its established bioequivalence to dimethyl fumarate. It is expected that diroximel fumarate will exhibit similar efficacy and safety profiles as dimethyl fumarate, which has demonstrated significant reductions in relapse rates and the occurrence of new or enlarging T2 lesions.